Explosive or potentially explosive atmospheres occur where fine dust of combustable bulk materials accumulate and become a dust cloud with high concentrations. Any kind of ignition source like spark, overheating, exccessive friction might lead to hazardous dust explosion in the zone. Almost all flammable bulk materials that arise as a result of, or that are used during industrial proccesses, are combustible and can cause dust explosions under certain conditions. Examples of such bulk materials include coal, flour, sugar, cereals, wood, corn starch, aluminium, magnesium, cotton and certain plastics. These explosions may occur when the combustable dust suspends on air, accumulated on hot surfaces, slides through chutes or conveyed within pipes etc.
To decrease dust explosion risk to acceptable levels, industrial proccesses should be designed and operated carefully. ATEX directives which are prepared and published by EU Community, are used as guidelines and obligatory rules for manufacturers, system integrators and end users. Production lines should be designed with respect to ATEX regulations and directives.
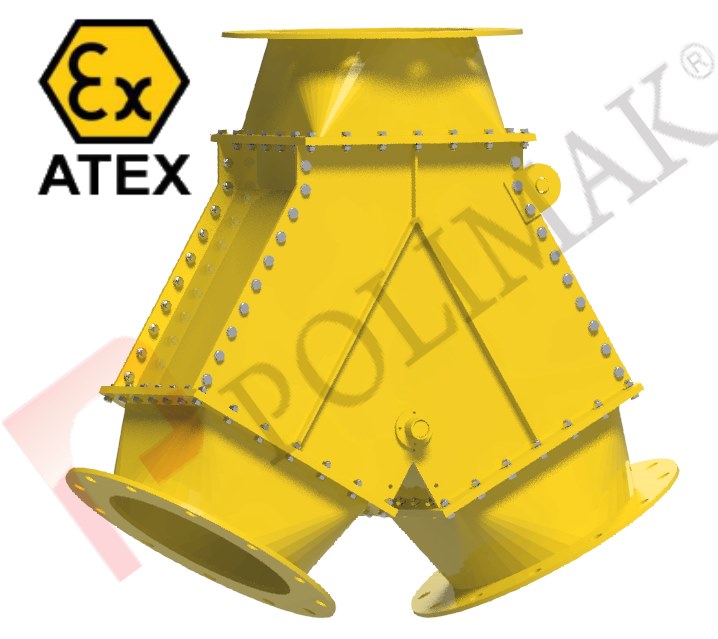



ATEX Certified Diverter and Flow Control Valves
For potentially explosive atmospheres, Polimak produces diverter and flow control valves with respect to ATEX directives 94/9/EC and 2014/34/EU. A great deal of know how is required to select proper type and configuration of diverter valves. All components of diverter valves are designed to isolate temperature, static electricity, spark and ignition sources from handled bulk material. Ex-proof electrical motors, Atex certified actuators, sensors, low friction bearings are used in these diverter valves to ensure process and environment safety.